About diabetes – long-term effects
Diabetes is when there is too much glucose in the blood. Gradually, high blood glucose levels start damaging the body’s organs. Possible long-term effects may involve damage to:
- large (macrovascular) blood vessels
- small (microvascular) blood vessels.
This causes heart attack, stroke, and diseases of kidneys, eyes, gums, feet and nerves.
Lowering the chronic effects of diabetes
A person can reduce the risk of the long-term effects of diabetes. This is possible by keeping blood pressure, blood glucose and cholesterol levels within limits. Also, eating healthy, healthy weight, lowering alcohol intake, and not smoking reduces the risk. Regular check-ups and screening are vital to pick up any issues early.
Diabetes and healthy eating
If a person is diabetic, he or she must include nutritious and healthy foods in diet. Also, he or she must avoid snacking on sugary foods. There are a range of foods available in each food group. Diabetics must have lots of fibre, less fat and less salt.
Alcohol consumption and diabetes
Limit alcohol consumption. A person must have no more than two standard drinks per day. Pregnant or breastfeeding females must completely avoid alcohol.
Diabetes and healthy weight
Losing weight is very important in obese people. That too, around the abdomen. It helps to reduce the blood pressure, blood glucose and cholesterol levels.
Diabetes and exercise
Be as active as possible. It is advisable to exercise at least 30 minutes a day. If a person is unable to do physical activity like walking, gym work, then consider:
- water aerobics
- chair exercises
- strength resistance training with light weights.
Smoking and diabetes
Smoking is the single lifestyle risk factor for developing diabetes complications. Smoking affects circulation by enhancing heart rate and blood pressure. It also narrows down the small blood vessels. Also, smoking makes blood cells and blood vessel walls sticky. It also accumulates the dangerous fatty material in the blood vessels. This may result in heart attack, stroke and other blood vessel problems. Diabetics who smoke have higher blood glucose levels than non-smokers with diabetes.
Regular diabetes screening checks
Regular checks should be done for:
- blood pressure
- blood glucose levels
- cholesterol and triglycerides
- kidney function
- eyes
Blood pressure checks
Regular checks for blood pressure are important at least twice a year. The normal blood pressure is under 130/80. Blood pressure control is very vital in decreasing the risk of diabetes complications.
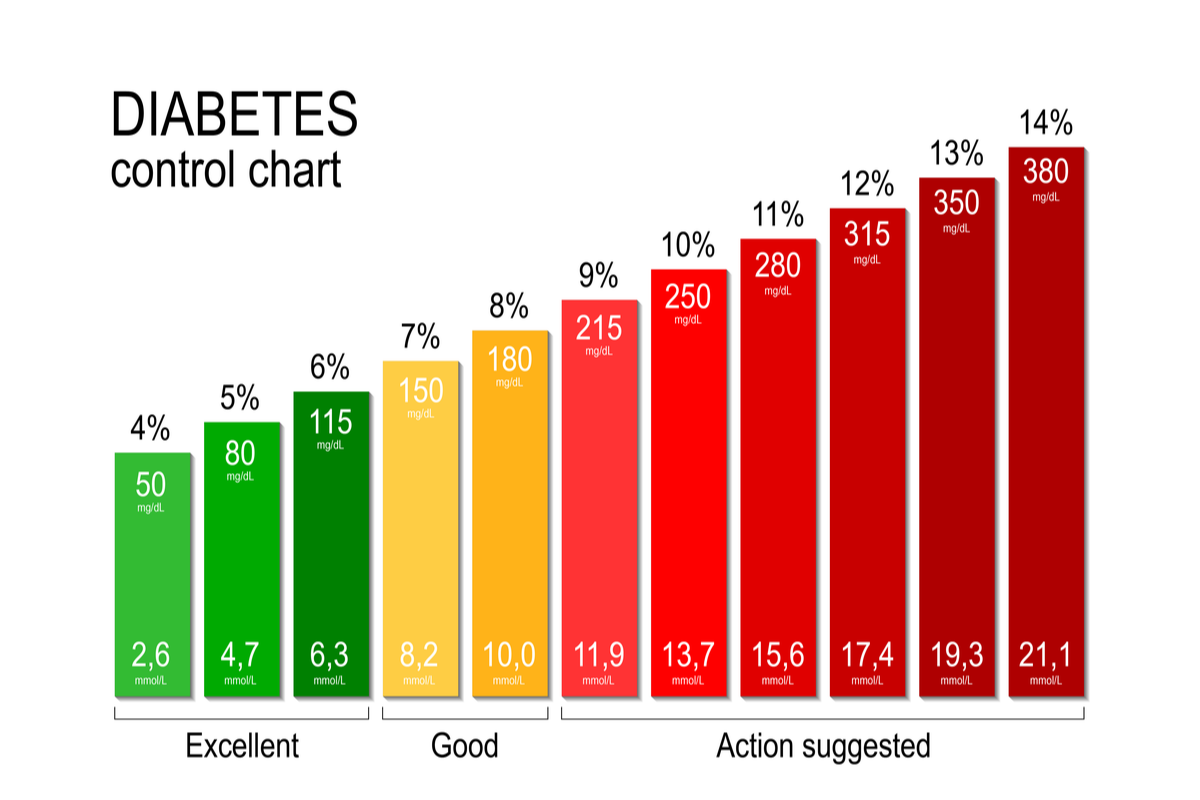
Blood glucose checks
Proper sugar control helps to decrease the risk of long-term diabetes-related health problems.
Cholesterol and triglyceride tests
It is a must to check cholesterol and triglyceride levels once a year. Aim for:
- total cholesterol less than 4.0 mmol/L
- triglycerides less than 2.0 mmol/L.
Long-term effects of diabetes
The most common chronic diabetes health problems are:
- damage to the large blood vessels of the heart, brain and legs (macrovascular complications)
- damage to the small blood vessels. This causes problems in the eyes, kidneys, feet and nerves (microvascular complications).
- Other body parts affected by diabetes: gut, skin, sexual organs, teeth and gums, and immune system.
Diabetes and cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease may involve blood vessel disease, heart attack and stroke. The risk of heart disease is higher in diabetic. Those who have increased cholesterol and blood pressure levels. Smoking, history of cardiovascular disease and being inactive also enhances the risk.
Eyes and diabetes
Diabetes-associated eye problems may involve: cataracts, retinopathy, glaucoma etc. Many people with damage to the eyes have no signs in the earlier stages. However, there are certain symptoms that may crop up and need urgent help. If a person has flashes of light, floaters, blots and dots or part of vision missing, visit a doctor.
Regular eye checks
It is vital to go for regular eye checkups if a person is diabetic. If retinopathy or another abnormality is present, eye tests are possible every year or more often as per ophthalmologist’s advice.
Kidneys and diabetes
Diabetics are at risk of kidney disease (nephropathy). This is due to the changes in the small blood vessels of the kidneys. Kidney disease is painless and do not result in symptoms until it is advanced.
Screening is very vital. Diagnosis of kidney damage occurs early by checking for microalbumin (very small amounts of protein) in the urine at least once a year. A doctor would also check the kidney function. This may include estimated glomerular filtration rate (e-GFR), with a blood test.
Nerves and diabetes
Nerve damage (neuropathy) results due to high blood glucose levels. To help avoid nerve damage:
- Keep the blood glucose levels in target range.
- If a person drinks alcohol, keep within the recommended limits.
- Don’t smoke.
Also read: These 11 Foods Can Help Improve Erectile Dysfunction